Chiral Center in Benzene Ring
So in this structure there are two chiral centers ie the 1st carbon atom and the 2nd carbon atom. Number the four atoms or groups of atoms such that 1 has the highest priority and 4 has the lowest priority.
How Can I Find The Chiral Centers In The Ring Stru Class 12 Chemistry Cbse
The benzene sector rule may be nsed to correlate the absolnte configuration of a contiguous chiral cento- of a monosnbstitnted benzene compound with the sign of the CE.

. So as it requireseven first condition is not. Electron withdrawing group attach to the benzene ring increases the reactivity towards nucleophilic substitution reaction Since -NO 2 group is strong electron withdrawing group. It is given below.
However the right benzene ring has two identical ortho substituents so the stable 90º dihedral angle conformer has a plane of symmetry. Because if I mirror them and place them on top of each other as I. All chiral twisted conformers are present as racemates so this compound cannot be resolved.
Point your thumb from the chiral center to the lowest priority group. A meso compound contains a plane of symmetry and so is achiral regardless of whether the molecule has a chiral center. Ths is achiral becauseit has planes.
If not chiral state why not. 3 points nter at is ader m at and b c a. Atomic number of the atom that is bonded directly to the chiral center.
That eliminates every atom except C1 and C3 of the ring. Bromine is the atom with the largest atomic number so this substituent is given the highest priority. Benzene is also a ring structure having a multiple bond system ie double bonds.
So in the ring structure we have to find which carbon atom is attached to four different compounds or elements. If they are different we can guess that it as a chiral carbon. The cis trans-14-dichlorocyclohexanes do not have any chiral centers since the two ring groups on the.
A stereocenter or stereogenic center is any point in a molecule bearing groups such that an interchanging of any two groups leads to a stereoisomer. Chlorine gets the number-two priority because it has a. A continuous crowdedness around the periphery is therefore of central importance for inducing.
The central benzene ring has no twist 0 torsion angle while the third-to-last benzene rings experience the largest twist 14 torsion angle. If you molecule does not have a chiral center draw a chiral carbon that has a carboxylic acid an amine a benzene ring and an Hattached to it -1-6---6-T-9 Below is the Lewis structure you drew previously. Chiral center means the carbon atom in the system that has all the different substituents.
Flipping structures often result in drawing the enantiomer when one tries to place the lowest priority group in the rear. It is given below. These include CH 2CH 3 and NH 2 groups oxygens halogens and any atom that is part of a double or triple bond.
If so indicate the stereogenic centers. Please explain why a benzene ring is achiral in terms of being superimposable. A chiral center is a type of stereogenic center.
The higher the atomic number the higher the priority. Ignore all atoms that cannot be chiral centres. In the above image the molecule has a hydrogen atom and a methyl group attached to the same carbon atom.
Benzene is also a ring structure having a multiple bond system ie double bonds. Ctu H2N OH symmety s superimposable. It belongs to the BTEX family Benzene Toluene.
Hydrogen has the smallest atomic number so its given the lowest priority. Benzene also known as benzol is one such common VOC identified by its unique numerical CAS2 number 71-42-2. Curve your fingers so that they point in the direction 1 -- 2 -- 3.
Atoms of the benzene ring are not chiral by definition cannot give rise to geometric isomers due to ring structure and cannot rotate to yield differing conformers. This can be explained with an example. But other two groups have formed a ring.
C-13 NMR or H-1 NMR. The first step is to prioritize all the substituents from one to four. Such a disrupted-helix conformation has a plane of symmetry and represents an achiral meso form.
It is also a hydrocarbon as you can see from the chemical formula of Benzene which is C6H6 represented diagrammatically as a ring commonly know as the Benzene Ring see opposite. If two or more of the atoms that are bonded directly to the chiral center are the same then. Double bonds - Assymetric centers.
Hence in basic medium ester containing -NO 2 group will be hydrolysed most easily. In an S N 1 reaction on chiral centres. Do benzene rings have chiral centers.
Pg133 Based on the CD-spectra of various optically active carbophanes a sector rule for the correlation of the sign of the 1Lb- Cotton effect of the benzene chromophore. Leave the structure where it is and use your hands to determine chirality. By definition a molecule thats not superimposable on its mirror image is a chiral molecule.
Here are the steps to find the chiral centres. The substituent however contains a chiral center an asymmetrically substituted CC and has sp3 hybridized carbon atoms that can exist in different conformational extremes. A plane of symmetry is a plane that cuts a molecule in half yielding two halves that are mirror reflections of each other.
However assuming it is a benzene ring then there is no chiral centre Its not aromatic its just a normal cyclic ring with a carbon bonded to both the 3 and 6 carbons. Chiral center means the carbon atom in the system that has all the different substituents. Now choose two structural features of your molecule and discuss how you would determine their presence using either IR.
For the remaining atoms check if there are four. To answer the OP its both the carbons mentioned above that are chiral as the cycle is not symetrical. First determine whether the groups attached to the carbon atom are different from each other.
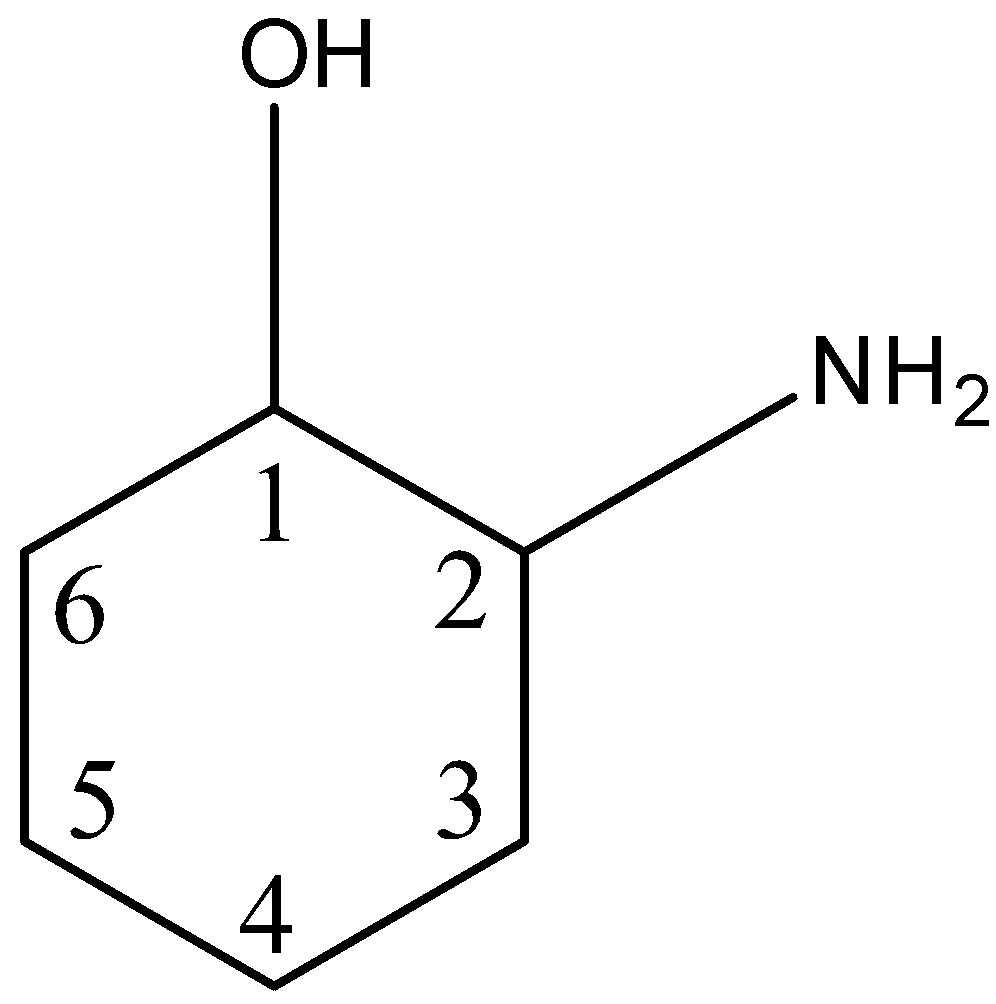
How Can I Find The Chiral Centers In The Ring Stru Class 12 Chemistry Cbse
Chiral Center Answers Ochempal

Comments
Post a Comment